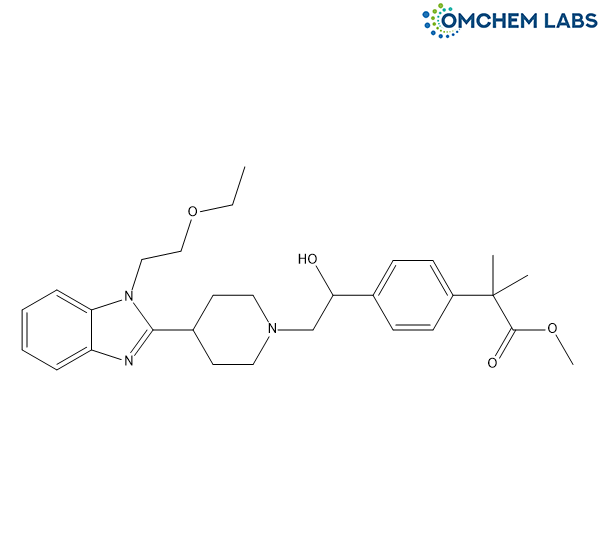
1'-Hydroxy Bilastine Methyl Ester
| Catalogue No |
BILA-OCL-012 |
| CAS NO |
1638785-21-3 |
| Molecular Formula | C29H39N3O4 |
| Molecular weight | 493.65 |
| Inquiry Status | In Progress |
| Synonyms | Methyl 2-(4-(2-(4-(1-(2-ethoxyethyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)piperidin-1-yl)-1-hydroxyethyl)phenyl)-2-methylpropanoate |
Detailed Overview of this Impurity: Discover more about Impurity Standard & Analysis
Impurity Profiling of 1′-Hydroxy Bilastine Methyl Ester: Scientific Considerations in Identification and Control
Introduction
Impurity profiling plays a pivotal role in the pharmaceutical development and regulatory evaluation of active pharmaceutical ingredients and their related substances. In the case of 1′-Hydroxy Bilastine Methyl Ester, comprehensive impurity assessment is necessary to ensure product consistency, safety, and compliance with international quality standards. Impurities, even when present at low levels, may influence the pharmacological behavior or stability of a drug substance. Therefore, systematic evaluation and control of impurities form an integral part of pharmaceutical quality assurance throughout the lifecycle of drug development.
Formation of Impurities During API Synthesis
The generation of impurities associated with 1′-Hydroxy Bilastine Methyl Ester can be attributed to multiple stages of the synthetic process. Chemical transformations involved in API synthesis often create opportunities for side reactions, incomplete conversions, or rearrangements that lead to structurally related impurities. Additionally, the use of reagents, catalysts, solvents, and intermediates may introduce process-related contaminants. Environmental factors such as exposure to moisture, light, or oxygen during synthesis and storage may further contribute to impurity formation through degradation or oxidation pathways. A clear understanding of the synthetic route is essential for anticipating and managing impurity development.
Analytical Data Interpretation Techniques
Accurate impurity profiling of 1′-Hydroxy Bilastine Methyl Ester relies on the application of advanced analytical methodologies combined with careful interpretation of analytical data. Techniques such as liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry, and spectroscopic analysis provide critical insights into impurity presence and behavior. Analytical data interpretation involves evaluating chromatographic separation patterns, spectral responses, and relative signal intensities to distinguish impurities from the primary compound. This process supports both qualitative identification and comparative assessment of impurity profiles across production batches, ensuring consistency and reliability.
Method Validation for Impurity Detection
To ensure the credibility of impurity-related analytical results, methods used for detecting impurities in 1′-Hydroxy Bilastine Methyl Ester must undergo thorough validation. Validation activities confirm that analytical procedures are suitable for their intended purpose and capable of consistently detecting impurities with acceptable accuracy and precision. Key considerations include method specificity, sensitivity, reproducibility, and robustness under varied analytical conditions. A validated method provides assurance that impurity monitoring is reliable and aligns with regulatory expectations for pharmaceutical quality control.
Purification Strategies for Reducing Impurities
Effective purification strategies are essential to minimize impurity levels associated with 1′-Hydroxy Bilastine Methyl Ester. Selection of purification techniques is guided by the chemical properties of both the target compound and the impurities present. Common approaches include selective crystallization, solvent-based separation techniques, and chromatographic purification. Optimizing purification conditions not only enhances the purity of the final product but also contributes to process efficiency and reproducibility. Proper purification is therefore a critical step in maintaining consistent quality across manufacturing batches.
Isolation and Characterization of Impurities
When impurities exceed identification thresholds or require structural confirmation, isolation and detailed characterization become necessary. Impurities related to 1′-Hydroxy Bilastine Methyl Ester can be isolated using preparative separation techniques designed to obtain sufficient material for analysis. Structural elucidation is typically performed using spectroscopic tools such as nuclear magnetic resonance, mass spectrometry, and infrared spectroscopy. Characterization of isolated impurities supports toxicological assessment, regulatory documentation, and the establishment of appropriate control strategies within the manufacturing process.
Conclusion
The impurity profiling of 1′-Hydroxy Bilastine Methyl Ester represents a comprehensive scientific effort encompassing impurity formation analysis, advanced analytical evaluation, validated detection methods, and effective purification and isolation strategies. Each element contributes to ensuring pharmaceutical quality, regulatory compliance, and patient safety. A well-defined impurity profiling strategy not only strengthens product reliability but also supports sustainable and controlled pharmaceutical development. Through systematic understanding and management of impurities, consistent quality of drug substances can be achieved throughout their lifecycle.